Is The Application Of Biological Techniques To Living Cells In Order To Alter Their Genetic Makeup.
Are you lot trying to end a negative mutation spreading and ruining your Biology marks? In this article, nosotros're going to guide you through Genetic Change so yous can selectively brood your marks up to an A+!
Module 6: Genetic Modify
This module expands on the knowledge yous gained from the previous Module 5: Heredity. It outlines the types of mutations that tin permanently alter Deoxyribonucleic acid and their overall affect on the organism.
The topics covered include:
- Topic 1: Mutation
- Topic 2: Biotechnology
- Topic three: Genetic Technologies
Topic 1: Mutation
A mutation is any permanent change in the Dna base sequence and typically occurs during DNA replication before prison cell division. Mutations can impact on cell activity, go unnoticed, give rise to different phenotypes or cause cancer in an organism. They can occur spontaneously within the jail cell or be induced by ecology factors (e.g. UV radiations).
There are two main types of mutations:
- Betoken mutations
- Chromosomal mutations
Bespeak mutations
Point mutations are gene mutations where 1 or more nitrogenous bases get altered in the DNA sequence of a factor. Types of point mutations include base exchange, insertion and deletion.
Base exchange can exist further divided into three categories including silent, nonsense and missense.
| Type of mutation | Detail |
| Silent Mutation | A codon is inverse for another codon which codes for the Aforementioned amino acid and thus has no consequence on the protein beingness produced.Eastward.g. AGG → CGG both code for the amino acid arginine. |
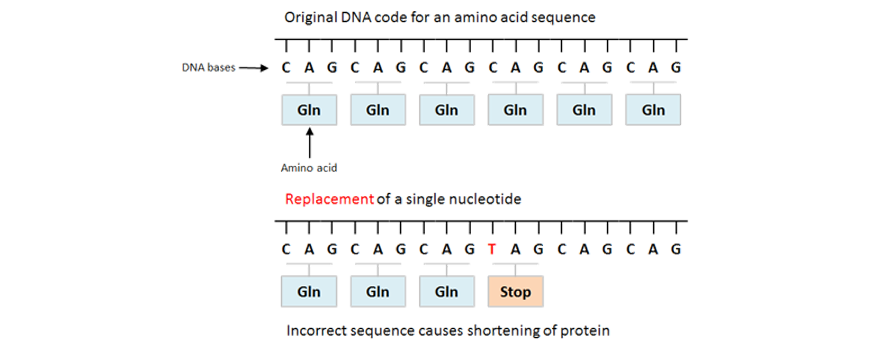
| Nonsense Mutation | A codon is changed to a Stop codon signalling early termination of poly peptide synthesis thus causing non-functional poly peptide to be produced. |
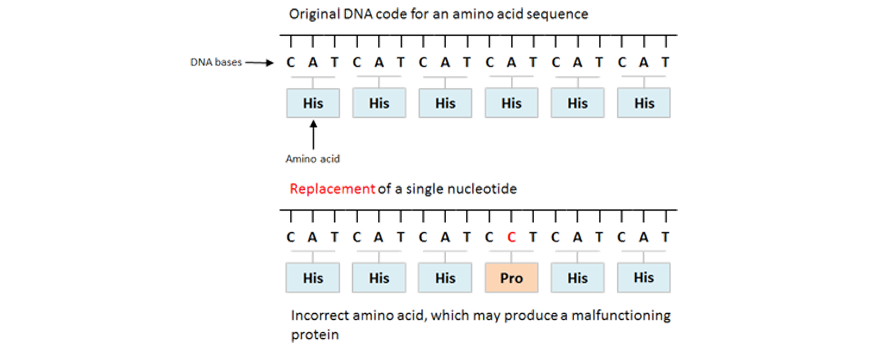
| Missense Mutation | A codon is changed to ANOTHER codon which encodes for a DIFFERENT amino acrid producing an altered poly peptide such as in sickle cell anaemia! |
Insertion and deletion of nucleotides in the DNA sequence crusade frameshift mutations that alter the overall reading frame of the gene by the mutation, producing contradistinct proteins as a event.
Chromosomal mutations
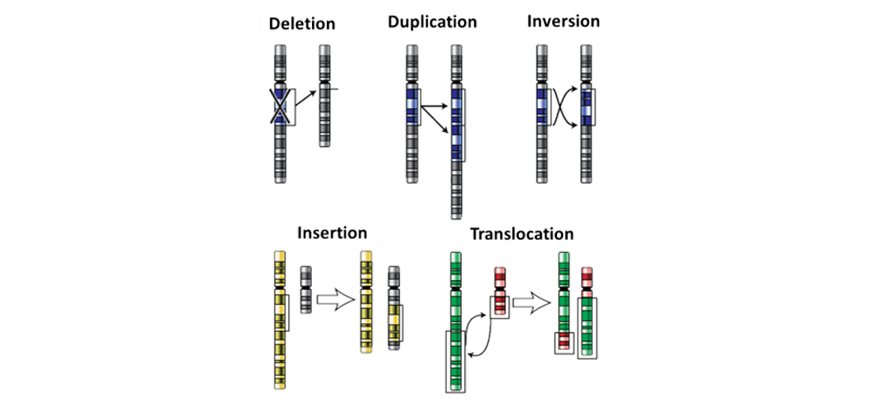
Chromosomal Mutations are mutations that alter the structure or number of chromosomes. Chromosomal Mutations affecting the Structure of chromosomes (block mutations) include:
- Insertion of a segment of i chromosome into some other chromosome.
- Deletion occurs when a chromosome segment breaks off and is permanently deleted.
- Inversion where a segment of a chromosome breaks off and is inverted earlier being re-inserted into its original chromosome.
- Duplication is a segment of a chromosome that is copied twice and may remain on the same chromosome or attaches onto a homologous chromosome.
- Translocation is a segment of a chromosome being exchanged with another non-homologous chromosome segment.
Chromosomal mutations affecting the NUMBER of chromosomes are caused by non-disjunction which occurs during cell division and is a consequence of chromosomes non separating properly into the gametes.
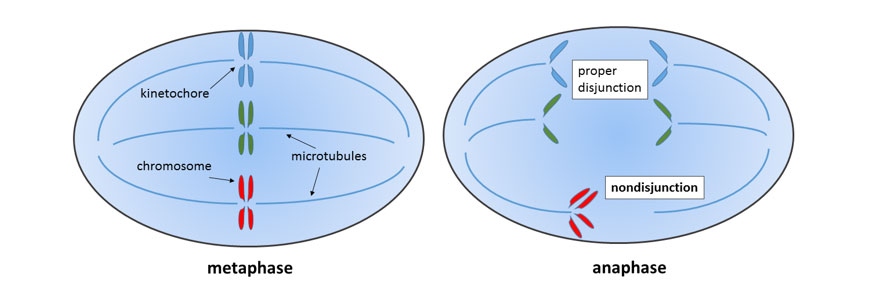
By Wpeissner – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/alphabetize.php?curid=32332257
Trisomy occurs when there is an actress copy of the Same chromosome. Down's syndrome is a common upshot of Trisomy 21 where there are 3 copies of chromosome 21 instead of two in the offspring.
Polyploidy occurs when in that location are extra sets of chromosomes, eastward.yard. instead of being diploid (2N), the offspring is triploid (3N) or tetraploid (4N). This type of mutation is fatal in humans, only can exist useful in ingather plants as it gives rise to traits such as large seedless fruits.
Mutagens are the cause of induced mutations and there are a multifariousness of types:
- Physical, such as electromagnetic radiation
- Chemical, such equally the chemicals in tobacco smoke.
- Biological, such as the Man Papilloma Virus (HPV).
The touch on of mutations will depend on whether the mutation occurs in a somatic or gametic cell. Somatic cell mutations occur in torso cells affecting but the private organism in which the mutation occurred in. Germ-line mutations occur in gametic cells (sperm or egg) and tin exist passed on to the offspring.

The affect of a mutation also depends on whether it occurs in the coding or non-coding DNA regions. A mutation in a coding region disrupts gene function and is likely to alter a protein product. A mutation on non-coding DNA is less likely to accept an touch and is more probable to be passed on to the adjacent generation.
Need last-infinitesimal HSC Biology help?
Don't leave it to the concluding minute, get skillful aid now! Learn more about our Matrix+ Biology HSC Prep Grade.
Topic 2: Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the area of biology that uses living systems or organisms to develop or modify products to benefit mankind. Diverse past uses of biotechnology include:
- Fermentation – microbes are encouraged to eat saccharide and produce useful products such as carbon dioxide and booze.
- Antibiotics – in the past mouldy food and honey were applied to injuries due to their antibody properties.
- Selective breeding – plants or animals with useful characteristics are used for breeding. The useful feature becomes more common over time. New varieties of plants and animals are produced this style.

Selective convenance has produced a broad diverseness of cattle for man consumption.
Biotechnologies that were developed more recently include:
- Genetic screening – Babies or adults tin have their genome tested for genetic diseases.
- CRISPR-Cas9 – The Cas9 enzyme runs along the Dna of a living cell looking for a sequence that matches the guide sequence. Once the sequence is found, the enzyme cuts the Dna. Past changing the guide sequence scientists can employ CRISPR-Cas9 to turn off genes.
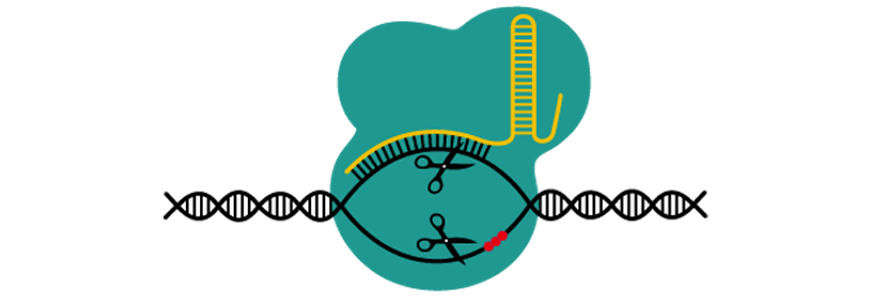
- Gene therapy – Used for diseases caused by a unmarried gene mutation, viruses or liposomes are used to deliver the normal version of the cistron into the patients' cells.
- Stem cell treatments – Stalk cells are undifferentiated cells that tin can exist stimulated to go whatsoever type of cell. This is useful for repairing damaged tissue and malfunctioning cells.
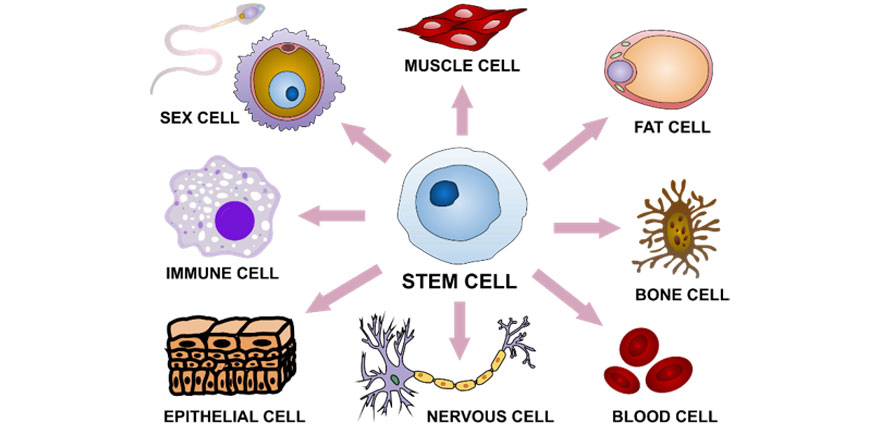
By Haileyfournier – Own piece of work incorporating, CC Past-SA four.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=79503487
Future directions for biotechnology could include:
- Using somatic cell nuclear transfer and a surrogate species to bring dorsum species that are extinct (de-extinction).
- Use of nanoscience in agriculture to detect beast and establish pathogens or deliver pesticides to improve food.
- Pharmacogenomics where drugs can be engineered for each patient's genetic makeup to maximise handling.
- Factor drives that ensure that two copies of a modified gene are passed on to all descendants rather than following normal patterns of inheritance.
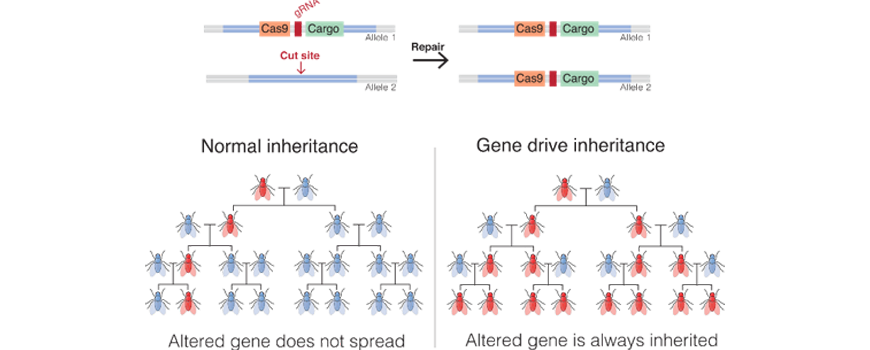
By Mariuswalter – Ain piece of work, CC By-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/westward/index.php?curid=62766590
While the use of modern biotechnology is incredibly useful, it is not without its issues. With the expansion of genetic screening, there is concern about who has admission to someone's personal genetic information and whether information technology could exist used to discriminate against them. This applied science can likewise be used to screen embryos and select ones with 'favourable' characteristics in an unethical way.
Similarly, CRISPR-cas9 tin be used to modify the genes of an embryo with unpredictable consequences (eastward.g. new mutations). Many of these biotechnologies are also expensive and then are not equally available to anybody, exacerbating existing inequality.
CRISPR-Cas9 offers potential cures for illnesses similar haemophillia. Only it is besides a applied science that raises upstanding dillemas and has already seen misuse by some researchers who altered genes in human embryos.
Fifty-fifty simple biotechnology such every bit selective breeding can be useful for humans but may affect the welfare of the animal. For case, Belgian blue cattle have been selected for a mutation that gives them extra muscle mass, simply as a issue they cannot give birth naturally and endure from many health issues.

Topic three: Genetic Technologies
Artificial insemination involves the assisted placement of sperm into the female reproductive tract in animals. It be used for medical or agronomical purposes (e.g. cattle breeding). Bogus pollination is the assisted transfer of pollen from the male person part of a flower to the female person office of the flower in plants. It is used to selectively breed plants with desirable traits such equally higher crop yield.
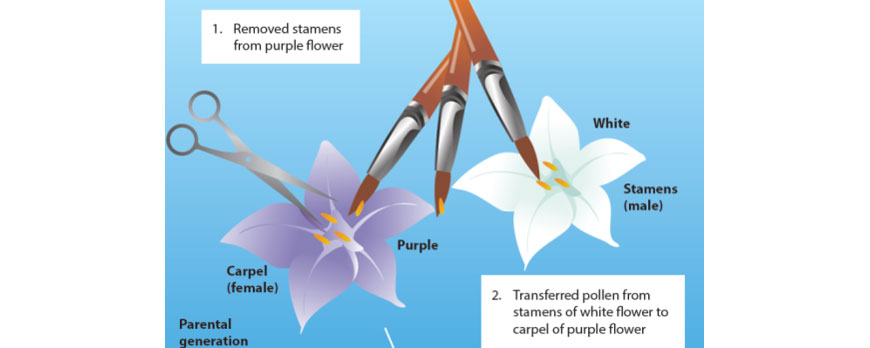
Both practices increment genetic variability by allowing crosses that would never have occurred naturally due to altitude or time factors. All the same, they subtract variability and thus Globe biodiversity long term as the same traits are selected for every time and the same male may exist used many times.
Cloning is a process that involves making an exact copy of genetic material. It includes:
- Cistron cloning, where many copies are fabricated of a single gene.
- Whole organism cloning, where genetically identical copies are fabricated of an private.
Whole organism cloning is achieved by somatic jail cell nuclear transfer where the nucleus is taken from a somatic cell of the organism to be cloned and inserted into an egg from a unlike private (that has had the nucleus removed).
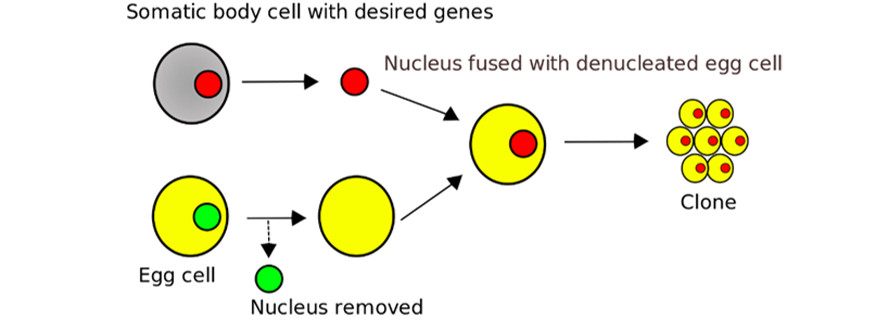
By en: converted to SVG by Belkorin, modified and translated by Wikibob – derived from image drawn by / de: Quelle: Zeichner: Schorschski / Dr. Jürgen Groth, with text translated, CC By-SA iii.0, https://eatables.wikimedia.org/west/alphabetize.php?curid=3080344
Factor cloning can exist achieved through recombinant Dna – an artificially created DNA sequence accomplished by combining two or more than DNA segments that do not usually occur adjacent to i another. Recombinant DNA can be used in multiple fields including agriculture and medical applications.
DNA segments from different species are sometimes integrated in this way in order to produce a transgenic organism. For case, Bt cotton is a transgenic organism has been modified to produce its ain pesticide in social club to maximize yield. Insulin can be produced by transgenic leaner containing the human gene for insulin, every bit shown below.
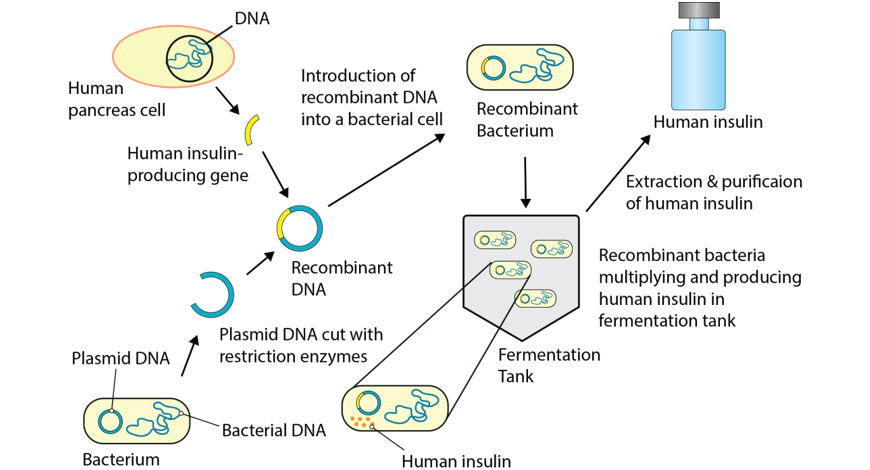
Creating transgenic species has many benefits for agriculture, medicine and industry. All the same, their utilise has raised many social and ethical questions:
- Are transgenic foods condom to consume? Should they be labelled?
- Is it ethical to change the Dna of an organism in this way?
- Exercise transgenic organisms create fauna welfare issues?
- What are the impacts on biodiversity and the surroundings?
- Is there a harmful relationship betwixt agribusiness and farmers?
Golden rice is a genetically modified crop with a factor from corn which is intended to increase its Vitamin A content for improved diet. While this production has the capacity to relieve millions of lives, there are concerns for its safety, profitability, impact on the environment and effectiveness.
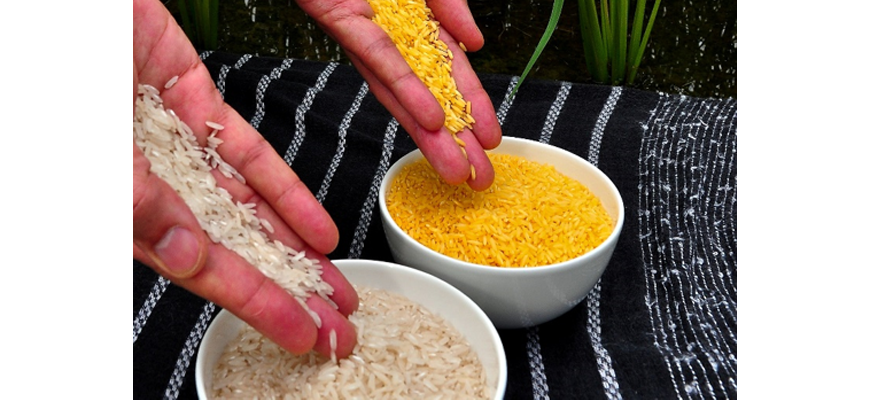

Golden rice side-by-side with jasmine rice
The biotechnologies covered in module 6 have an touch on on genetic, species and ecosystem biodiversity.
| Biotechnology | Bear upon on biodiversity |
| Selective breeding | Decreases genetic multifariousness past inbreeding to create homozygous individuals. Leaves the species vulnerable to diseases. |
| Monoculture | Decreases species and ecosystem diverseness past growing a single species over a large area. |
| Artificial insemination | Increases genetic diversity past crossing individuals that would not practise and so naturally. Decreases genetic diverseness if the same male is used many times. |
| Artificial pollination | Increases genetic variety by crossing individuals that would not do and then naturally. Decreases genetic multifariousness if the same male is used many times. |
| Whole organism cloning | Decreases genetic diversity in a population by creating genetically identical copies. |
| Transgenic organisms | Increases genetic diverseness past inserting genes from a different species. Even so, transgenic organisms are oftentimes cloned. Transgenic organisms are given a genetic advantage that may permit them to out-compete other species. |
© Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au, 2022. Unauthorised use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site's writer and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may exist used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.
Source: https://www.matrix.edu.au/beginners-guide-year-12-biology/genetic-change/
Posted by: adkinscomay1980.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Is The Application Of Biological Techniques To Living Cells In Order To Alter Their Genetic Makeup."
Post a Comment