Is 414w Draw To Close To A 500w Power Supply?
Every unmarried desktop PC, console, or laptop has one of these. It doesn't boost your frame charge per unit or churn out cryptocurrency; it doesn't have billions of transistors and it'south not made using the latest semiconductor process node. Sounds boring, right? Not at all! This thing is super of import because without it, our computers would practice admittedly nothing.
Power supply units don't break headlines like the latest CPUs do, but they're awesome pieces of engineering. So let's put on our gowns, masks, and gloves, and pull open up the apprehensive PSU -- breaking down its various parts and seeing what each fleck does.
What'south the proper name of the game?
Lots of computer parts accept names that require a fleck of technology cognition to understand exactly what it does (e.yard. solid land drive) but in the case of a power supply unit of measurement, information technology's pretty obvious. It'southward a unit of measurement. Information technology supplies power!
Since we can't only dust off our hands and proudly say 'article done' with that kind of statement, nosotros better starting time having a look at ane. We're using a Cooler Master G650M -- it's a fairly generic pattern, with a specification found in dozens more like it, merely it sports one item feature that non every power supply unit of measurement has.
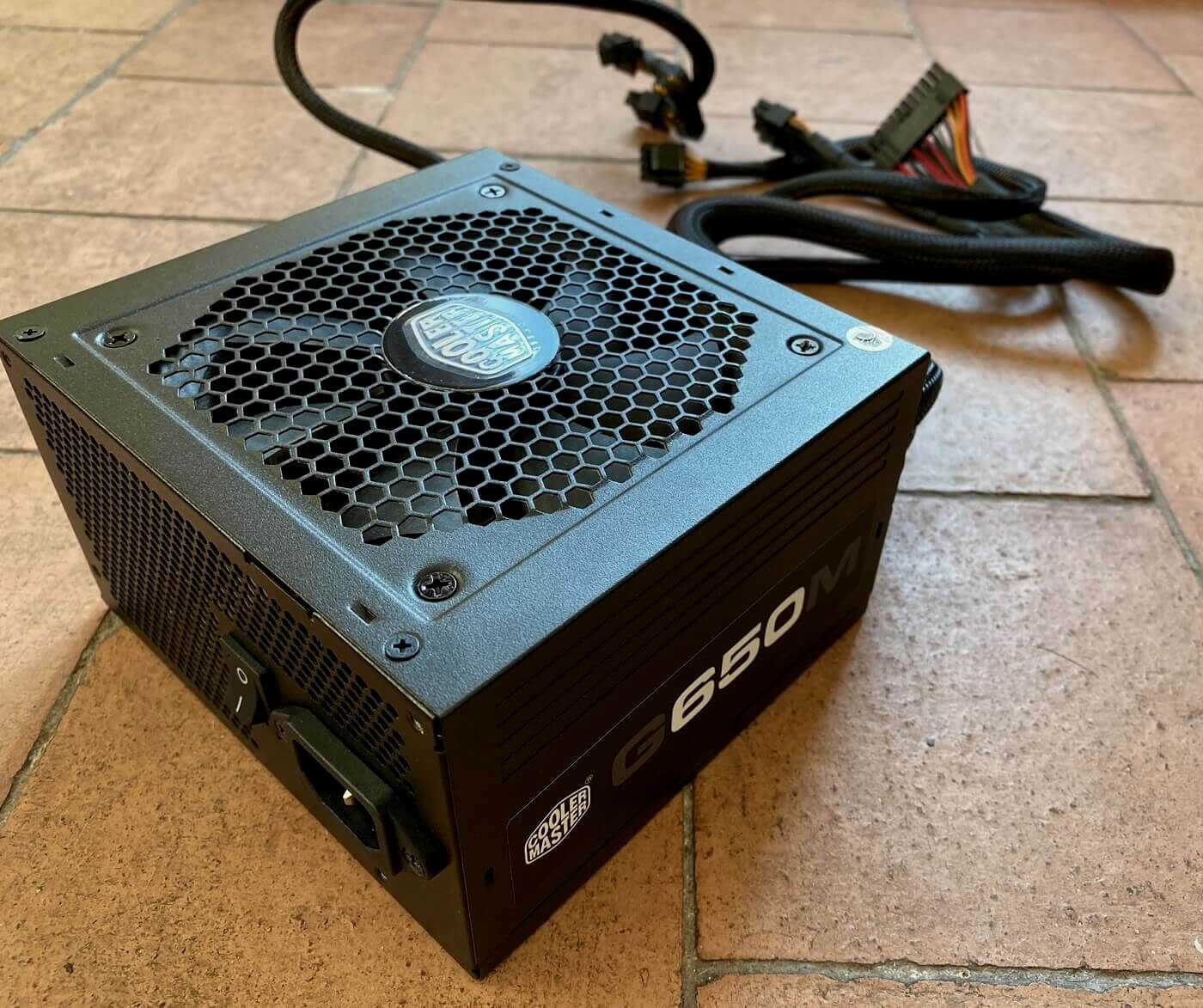

This PSU is a standard-sized 1 and by that we mean it complies with the ATX 12V v2.31 grade gene, and so it fits inside lots of computer cases.
There are other form factors, though: ones for smaller cases or unique ones for specific vendors. Not every unit follows the exact sizes set up past the standard course factors, they might be the same width and height, merely they could be longer or shorter.

They're as well usually labelled past how much power they tin can supply as a maximum; in the case of the Libation Master, information technology can provide up to 650 watts of electrical power. Nosotros'll come across what that actually means in this article, but you can get PSUs that deliver just a pocket-size number of watts, as not everything computer-wise needs hundreds of watts to run. The majority of desktop PCs will run fine in the range of 400 to 600 W, though.
PSUs like this one are contained within a metal box, commonly blackness or bare metallic, so they can be heavy. Laptops nearly always have a PSU that sits externally to the computer and is almost always plastic, but the insides are very like to what we'll run across in this one.
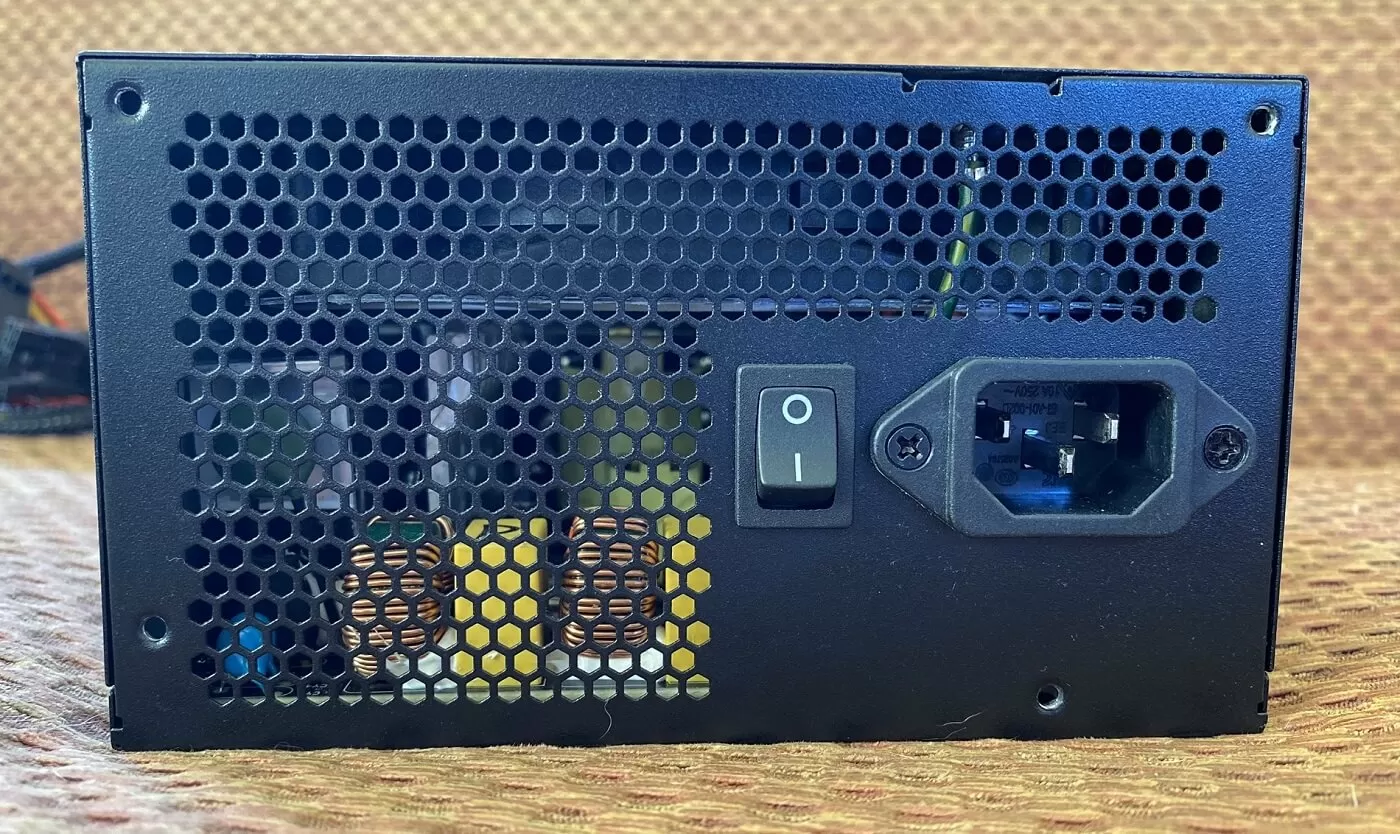

Most desktop PC power supplies come with a switch to isolate the mains electricity supply and a fan to keep things nice and cool, but not all do (or need to). Not all of them volition have a metallic body full of holes, either -- those found in servers rarely have them.
Merely every bit you tin meet in the film above, we've already taken a screwdriver to our example, and then permit's rip off the lid and jump within.
I'm back in blackness
Before we beginning rummaging near with the insides of a PSU, let's think about why we even need 1 in the starting time identify. Why can't nosotros take the computer connect directly into the mains outlet? The answer lies in the fact that modern computer parts are expecting the electric power to be delivered in a very different form to that provided by the outlet.
The graph beneath displays how mains electricity (U.s. = bluish and dark-green lines; UK = ruby-red line) is supposed to exist. The x-axis shows time in milliseconds and the y-axis shows voltage in volts. The all-time way to think almost voltage is that it's a measure of energy deviation between two points.
If a voltage is applied across a conducting material (e.g. a length of metal wire), the difference in free energy volition make electrons in the material flow from the higher energy level to the lower one. These are one of the edifice blocks of atoms, that make up the cloth, and metals have lots of electrons gratis to movement nearly. This flow of electrons is called a current and gets measured in amps.
I adept illustration for the techno-speak is that electricity can be thought to be similar water in a hose: voltage is akin to the pressure level y'all're using, the flow charge per unit of the water is the current, and whatsoever restrictions in the pipe acts the same as electrical resistance.
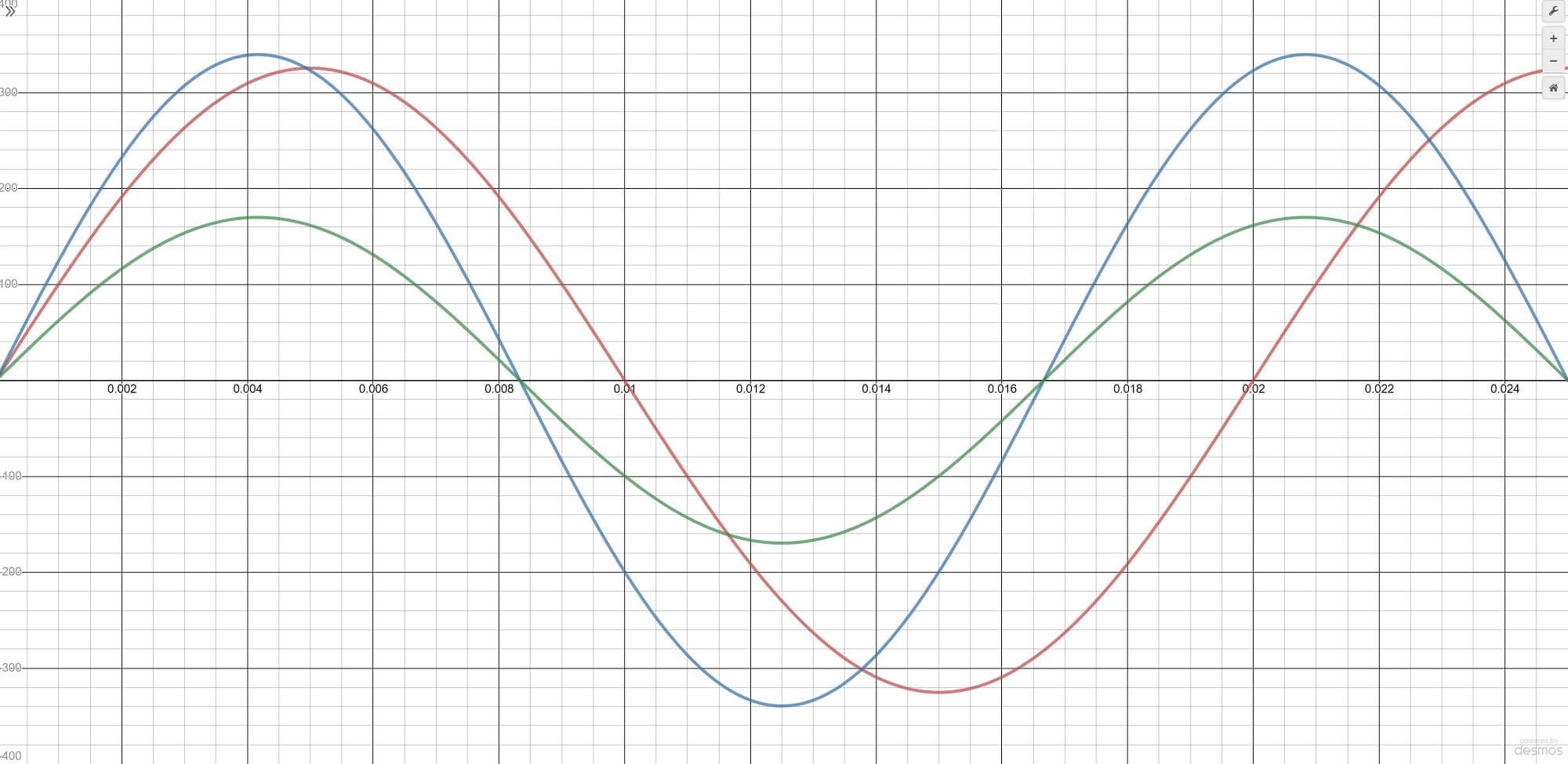
We can run into that mains electricity varies over time and this is known as an alternate electric current voltage supply - or just Air-conditioning, for short. In the US, the mains voltage alternates 60 times per second, reaching a tiptop of 340 V or 170 V, depending on the location and supply. The United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland hits a slightly lower height, and varies a little slower, also. Almost all countries around the world have mains outlet voltages like this, with just a few having lower or higher peak voltages.
The need for a PSU lies in the fact that computers don't work with AC: they need a abiding voltage, one that never changes, and it besides needs to be of much lower level. Using the same graph scales, information technology looks something like this:

It's so much lower that it's barely visible, but the requirements of a modern computer aren't for one constant voltage, just four - namely +12 volts, -12 volts, +5 volts, and +3.3 volts. And because these values are constant, they're called direct current or DC, for short. So a big part of what a PSU does, is convert AC to DC (cue the guitars...). Fourth dimension to open the unit and have a look at how it does this!
... a big part of what a PSU does, is convert AC to DC (cue the guitars...). Time to open the unit and have a await at how it does this!
At this stage, nosotros should warn yous to non attempt this if you don't know what you're doing. Messing most with the insides of a PSU tin be potentially very dangerous. There are components within every unit of measurement that store electrical energy, and some shop a lot.

The layout of this PSU is similar to many others, and although the make and model of the diverse parts used inside will be dissimilar, they fundamentally practise the same thing.
The mains outlet connection to the PSU is at the elevation-left manus corner of the picture and the supply essentially runs clockwise around the picture, until reaching the output of the PSU (big cluster of colored wires, bottom left-hand corner).
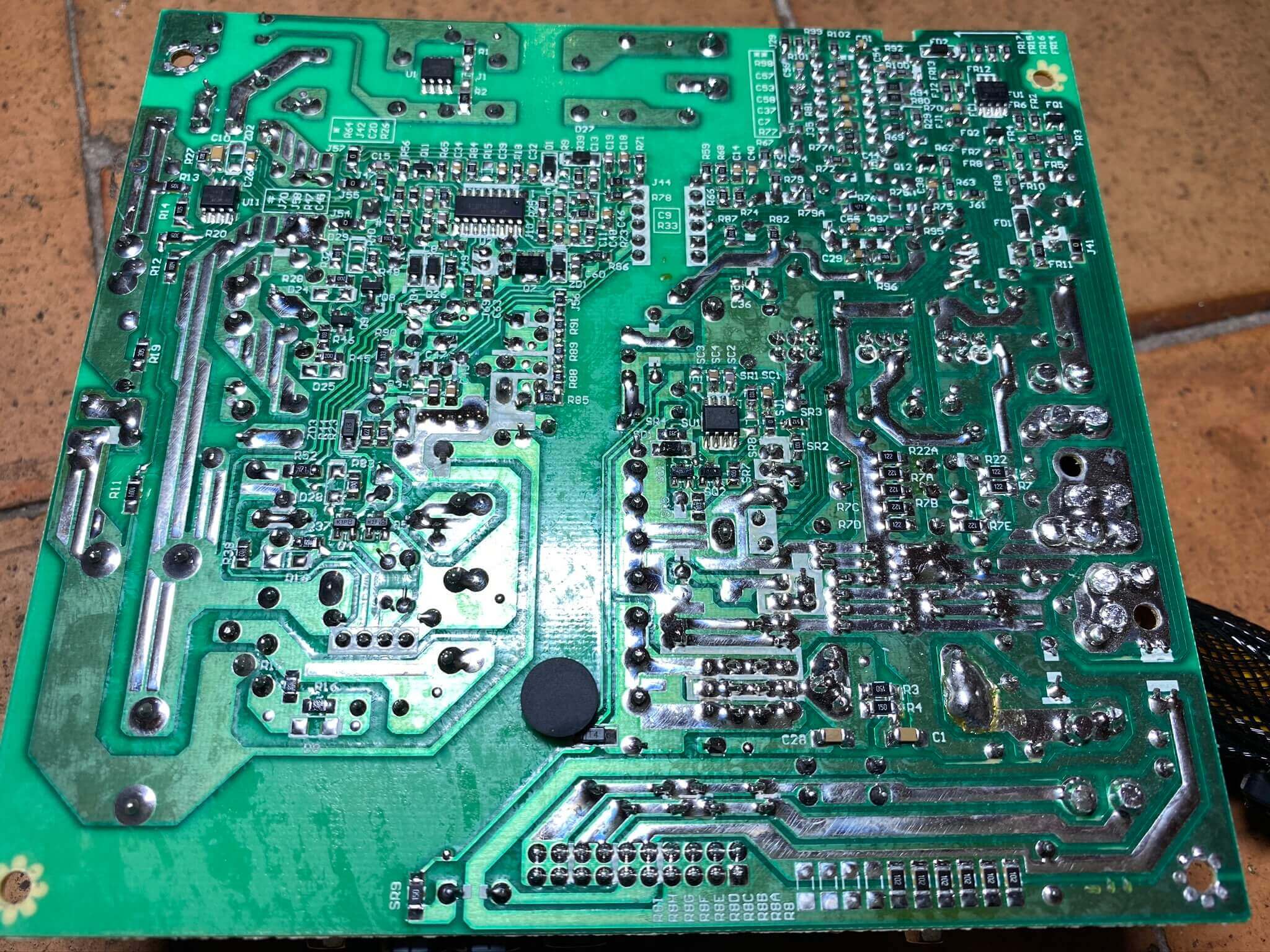
If we flip the circuit board over, we can see that compared to connections on a motherboard, these are broad and deep -- they're designed to have lots of electric current flowing through them. Something else that's immediately obvious is the big gap running down the middle, like a river cutting a path in a field.
This highlights the fact that all PSUs have ii conspicuously defined sections to them: master and secondary. The former is all about setting up the input voltage so that it can be efficiently changed from the mains supply level; the latter is everything nearly that alter and the processes afterward.
He's a smoothen operator
The very beginning thing the PSU does to the mains electricity isn't about changing it from Air conditioning to DC, or dropping voltage -- instead, it'due south all about smoothing out the input voltage. Because we have lots of electric devices in our homes, offices, and business that switch on and off, likewise as emit electromagnetic signals, the varying Air conditioning is often lumpy and with the occasional spikes (the length of the variations isn't constant either). Not only do these make it harder for the PSU to adjust the mains, it can besides damage some of the components within it.
This PSU has two stages of so-called transient filters, the first of which is direct applied to input socket, using 3 components called capacitors to exercise the job. Think of these equally being like a speed crash-land for sudden changes in the input voltage.
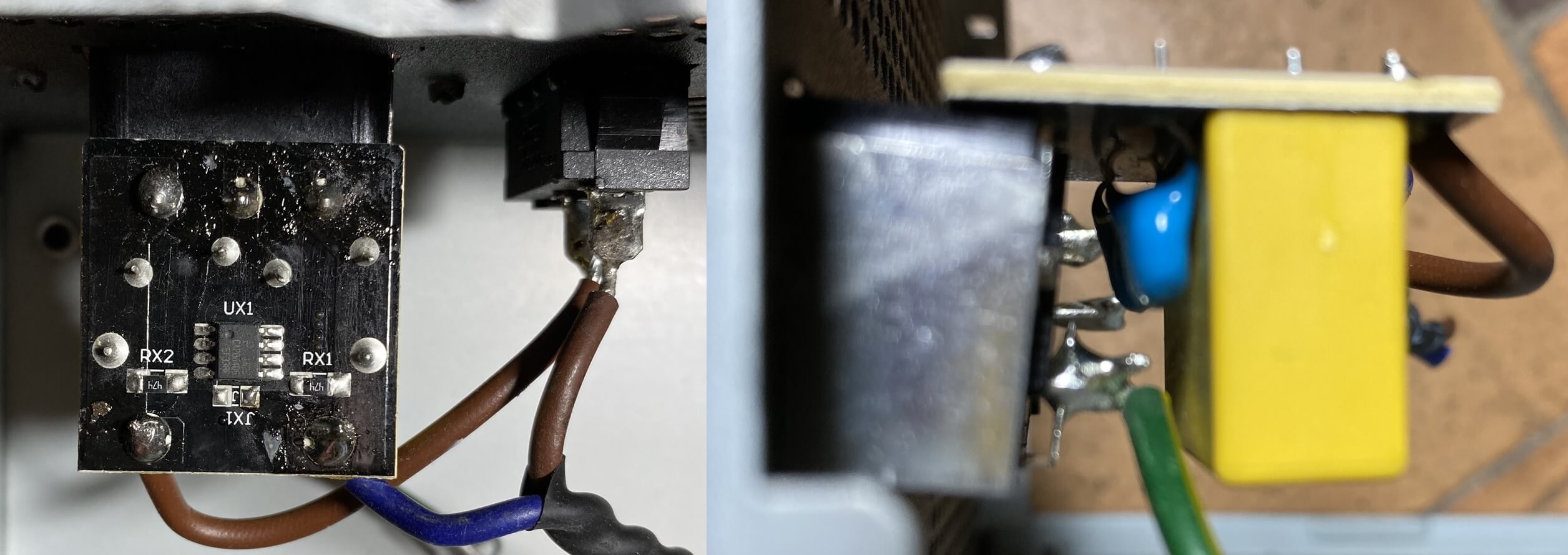
The second stage of filtering in this PSU is more complex, simply essentially does the same affair.
The xanthous blocks are more capacitors, whereas the greenish rings wrapped in copper wire are inductors (although they're usually called chokes when used this way). Inductors store electrical energy in a magnetic field but this field also 'pushes back' on the voltage supplying the energy -- and then a sudden spike in the voltage results in a sudden kicking back from the magnetic field to suppress it.
The two little blue discs are yet more capacitors and just below them (subconscious under a black plastic cover) is a metal oxide varistor (MOV). These are also used to assist counter jumps and spikes in the input voltage; yous can read more about unlike types of transient filter circuits hither.

This section of a PSU is often the get-go sign of where costs accept been cut to ensure the model hits a specific upkeep. Cheaper ones will have less filtering, and the cheapest of all will accept none at all (which is not what y'all desire!).
Now that nosotros're all smooth and chilled, let's get on with the twenty-four hours chore of a PSU: changing the voltage.
Rock downwards to electric avenue
Remember that the PSU needs to alter an Ac voltage that might exist averaging 120 volts (technically, it's root hateful squaring 120 volts, merely that doesn't exactly roll off the natural language) and hack that down into DC voltages of 12, five, and 3.three volts.
The beginning affair that gets done is an Air-conditioning to DC conversion, and this PSU uses a component chosen a bridge rectifier. In the picture beneath, this is the flat blackness object glued to the chunk of metal (which acts as a heatsink).
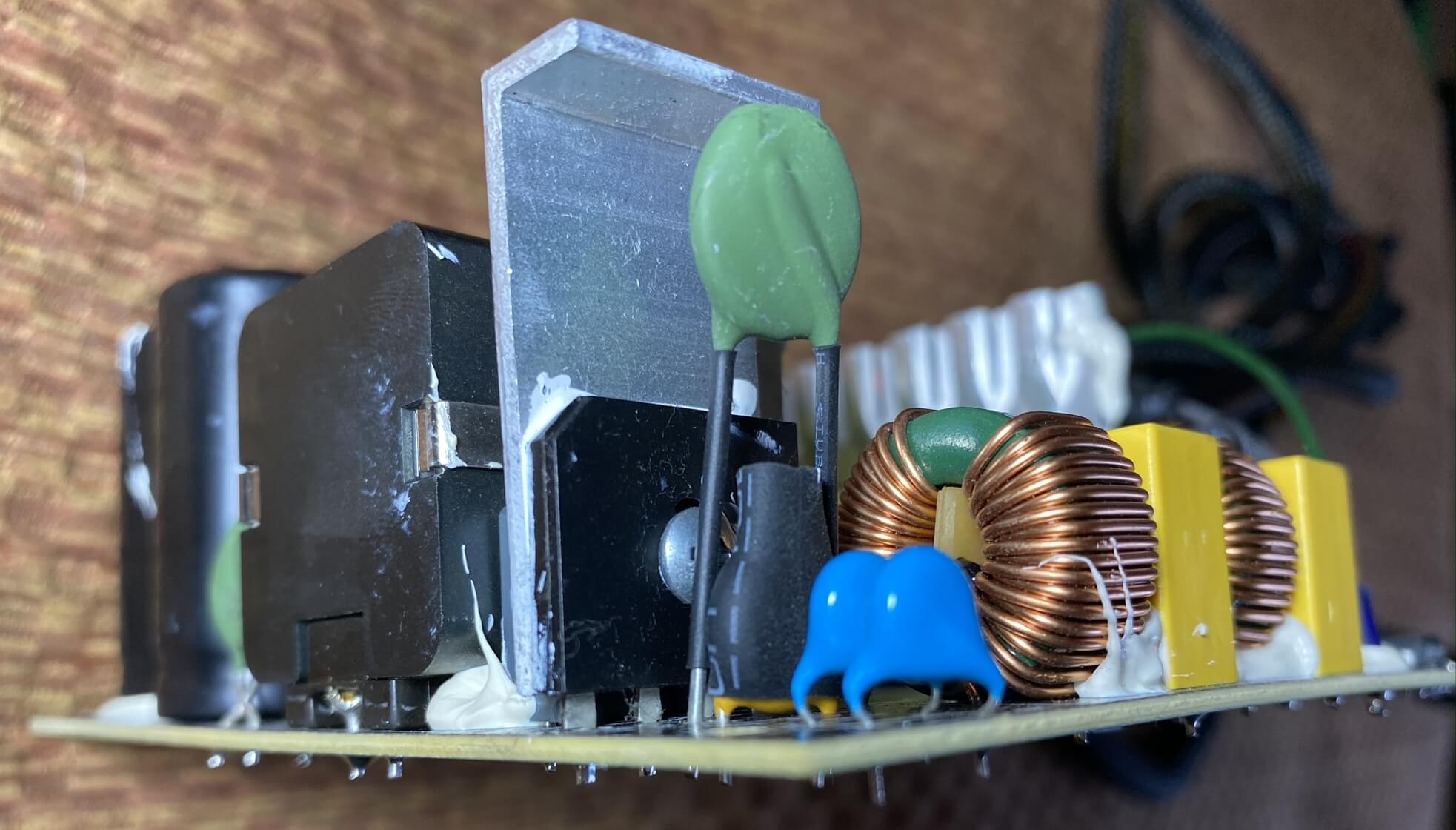
In one case again, this is some other area where a PSU manufacturer can cutting costs, with cheaper components doing a worse job of the AC-to-DC conversion (e.g. emitting more heat). Now, if the input voltage peaks at 170 volts (which is the case for 120V mains), then the bridge rectifier will output 170 volts DC.
This gets passed on to the next stage of the PSU and in the one nosotros're looking at, information technology's chosen an agile power factor correction converter (APFC). This circuit adjusts the current period in the unit to take into account that it is total of components that store and release energy in a circuitous way; this can result in the actual power output of the unit of measurement existence less that what you're supposed to be getting.
Other supply units use passive converters, that essentially practise the same job. They're less effective only fine for low power units -- they're besides cheaper, then you can gauge what kinds of PSUs have these, when they really shouldn't!

The APFC can be seen in the epitome in a higher place - those large cylinders on the left are capacitors and they store the adapted current, before sending them on to the next footstep in the PSU'southward concatenation of processes.
This department tucked behind the APFC is chosen a pulse width modulation excursion (PWM, for curt). Its chore is to take the DC voltage and utilize several field outcome transistors to switch the voltage on and off at a very high rate -- information technology essentially converts the DC voltage back into an Air-conditioning ane. It does this because the part of the PSU that turns the mains voltage right down into 12 volts is a transformer. These devices apply electromagnetic consecration and a set of two coils of wire (one having more loops in the coil than the other) to stride down the voltage; however, transformers only work with an alternating voltage.
The frequency of the Air conditioning voltage (the charge per unit at which information technology varies, measured in hertz, Hz) significantly affects how efficient the transformer is -- college is ameliorate -- which is why the 50/60 Hz mains supply gets changed into 1 that varies at something like 50/lx chiliad Hz. The more efficient a transformer is, the smaller information technology can be. This super fast switching of the DC voltage is the source of the name for this type of device: a switched mode power supply (SMPS).
You can see 3 transformers in the picture below - the largest generates just the 12 volt output; in other PSUs, the big transformer might brand all of the voltages. The next larger one creates a unmarried v volt output that we'll talk about in a bit, and the smallest one acts as an isolator for the PWM circuit, keeping it rubber from damage and too stopping it from causing interference with other voltages in the PSU.
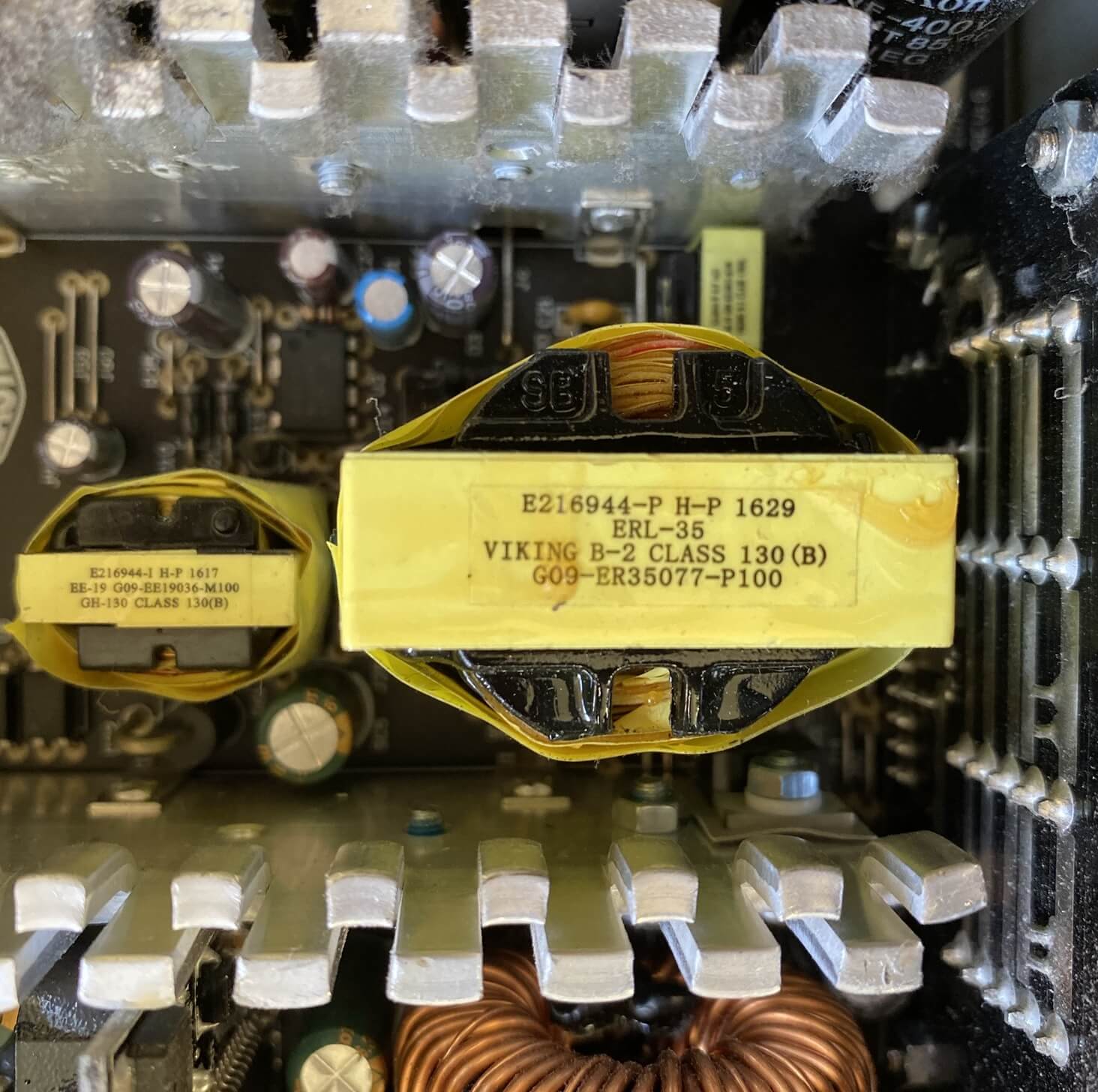
Various PSUs will have different means of creating the required voltages, isolating the PWM circuit, then on. Information technology'll all depend on budget constraints and how much ability the unit of measurement needs to offer. All of them, though, will need to take the output off the transformer and turn it dorsum into DC.
In the epitome below, the large chunk of metal is the heatsink for the bridge rectifiers that practice this conversion. We can also come across in this specific PSU, the circuit lath in the middle of the picture corresponds to a cluster of voltage regulation modules (VRMs) that create the 5 and 3.three volt outputs.

At this stage it'south worth talking about something called ripple.
In a perfect earth, with perfect PSUs, the varying AC voltage would be converted into a abiding, never-wavering DC voltage. In reality, though, information technology's non 100% spot on, and the DC voltages do vary e'er so slightly.
This variation is called the ripple voltage and for a PSU, you want information technology to be a small as possible. Cooler Master doesn't provide the size of the ripple voltage in the specifications for this PSU model, so we've turned to a detailed review to find them. 1 such analysis was done by JonnyGuru.com and they found that the +12V line in their tests had the ripple voltage peaking at 0.042 volts (42 millivolts).
The image beneath shows you how this compares to what is required. The ruby line is the targeted constant +12V DC, the varying blueish line is what nosotros're actually getting (although the ripple itself isn't constant).

The quality of the capacitors used throughout the PSU play a significant role. Smaller, cheaper ones would result in the ripple being bigger, which is not what nosotros want. If information technology'south likewise large, and then the complex electronic circuitry in the residuum of the estimator might operate in an unstable manner. Fortunately, in our example, forty-odd millivolts is okay: not great, simply swell.
No affair what is used to create the output voltages and ensure they're DC in form, at that place's still a few more $.25 of circuitry needed earlier nosotros start waving cables out the place. It all relates to managing the PSU'southward outputs, ensuring that if a high demand for power is taking identify on one detail voltage, then the others aren't going to be nobbled in the process.
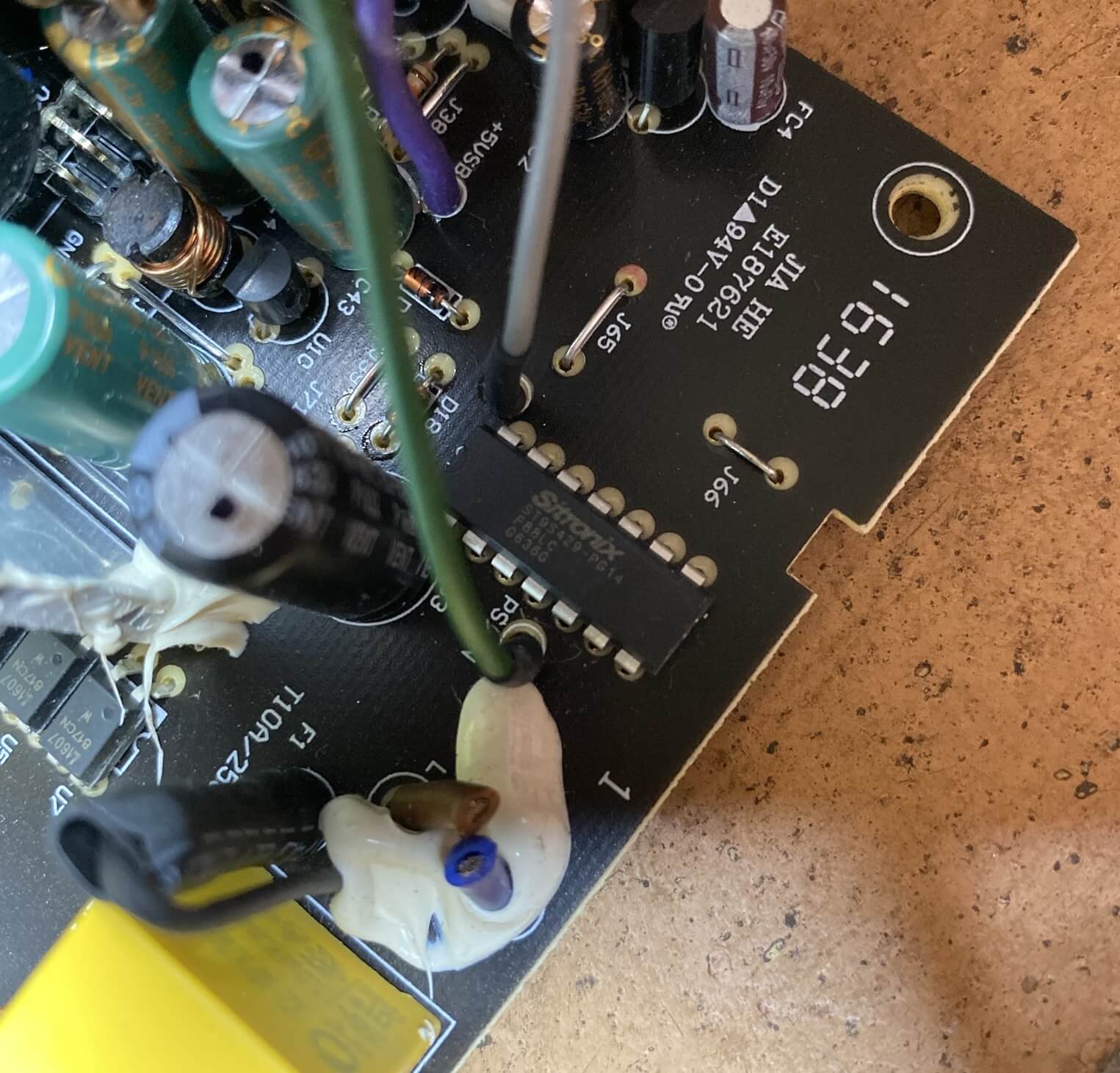

The chip you can see hither is called a supervisor and monitors the outputs, checking that they're not delivering too much or too niggling voltage and current. It's not very sophisticated, though, every bit all it does it shut off the PSU, if any of those problems occur.
More expensive supply units use digital indicate processors (DSPs) to monitor what's going on, and these can also adjust the voltages if required, as well every bit send details near the condition of the PSU to the computer using it. Not overly useful for the typical PC user, just for computers used as servers, compute machines, and then on, it'southward often a desired feature.
Plug in baby
All power supply units come with long bundles of wires, sprouting out of their back. The number of bundles, and how they're connecting to the chief unit will differ across the vast array of models bachelor, but they'll all provide some standard connections.
Since voltage is a mensurate of difference, there needs to be two wires for a given output: one for the indicated voltage (east.g. positive 12 volts, or +12V for short) and a reference wire that the difference is measured against. This wire is known as the basis or common line, and the 2 form a loop: running out the PSU, to the device needing the power, so back into the unit.
The period of current runs through these loop wires, but since some of the loops will only have a small amount of current flowing in them, several basis wires can be shared past unlike loops.

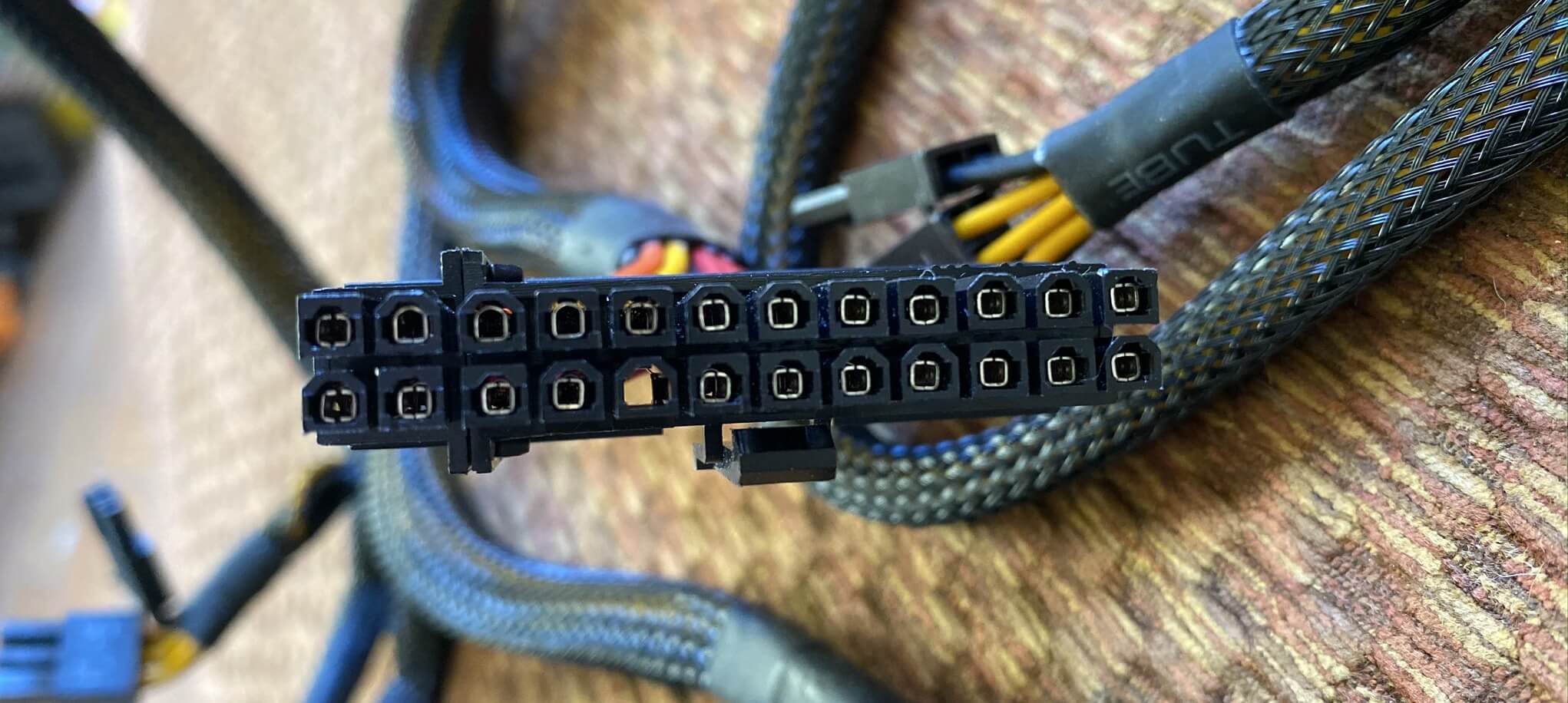
The start of which is the obligatory 24-pin ATX12V version 2.4 connexion - information technology offers multiple wires for the various voltages, plus a few specific ones.

An of import one is the +5V standby wire - for as long as the PSU is switched on and plugged in, this wire is e'er live. This is considering a computer doesn't really switch off, when you tell the operating arrangement to shut down. The motherboard draws the power it needs to remain agile off the standby connection.
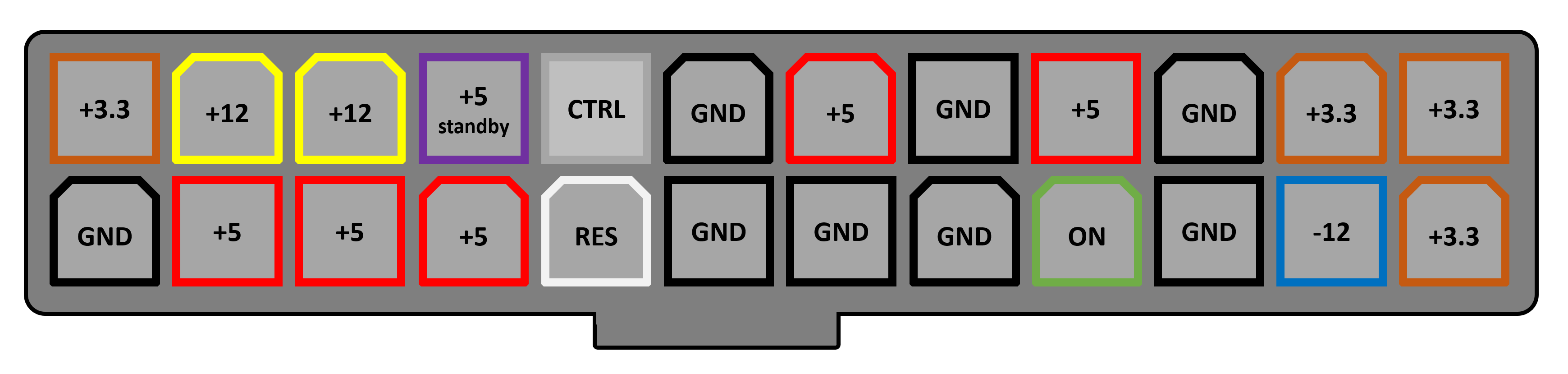
In that location volition likewise be another 8 pivot connector for the motherboard, that provides ii sets of +12V and ground wires, and most PSUs volition too provide at least i PCI Express 6 or 8-pin power connector.
Graphics cards can only take a maximum of 75W from the motherboard PCI Express slot, so this connector offers boosted power for today's monstrous GPUs.
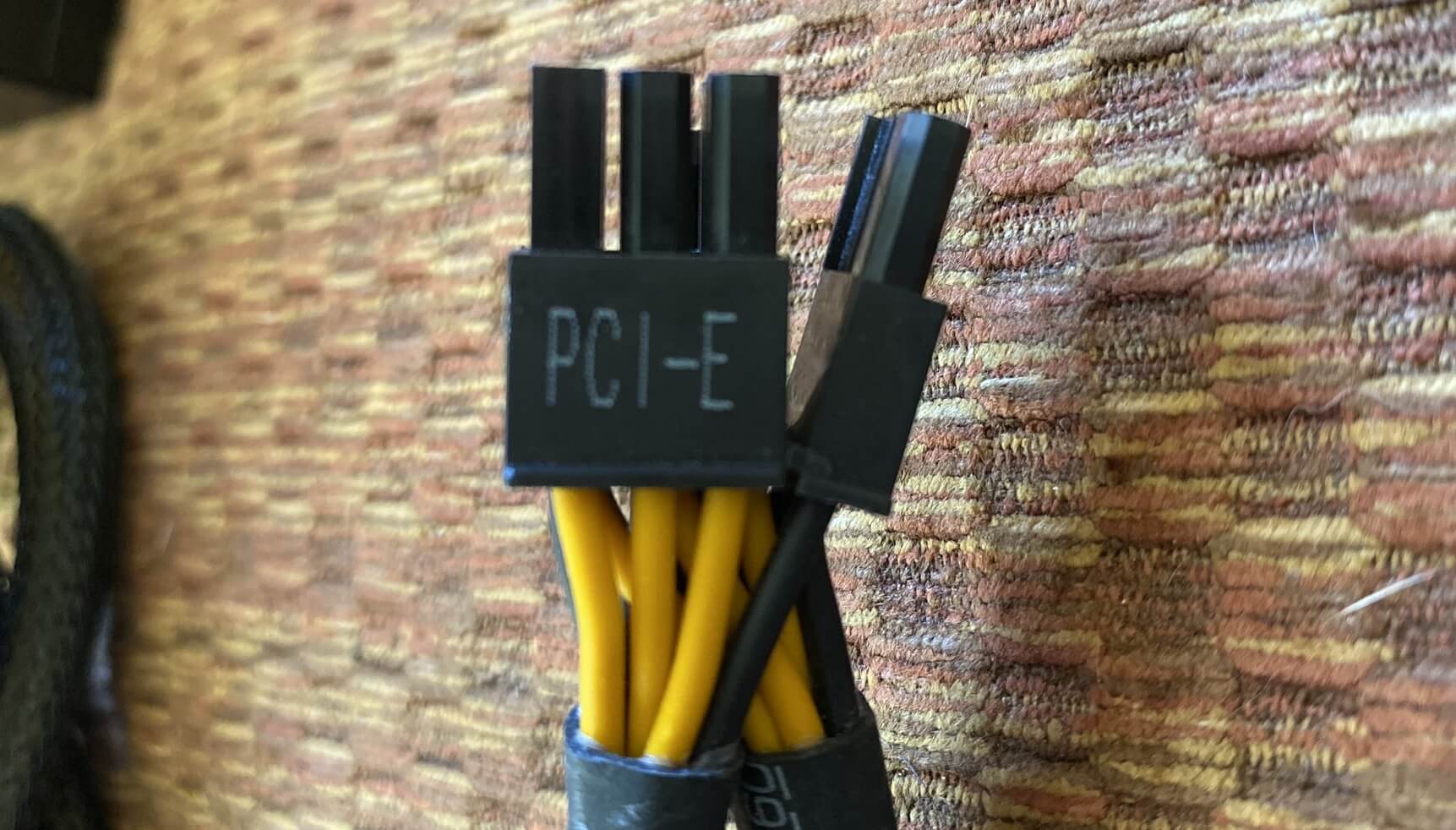

This detail PSU really runs two PCI Express power connectors off the same wires, for cost reasons, so if you had a really powerful graphics card in the reckoner, it would exist best to use a separate packet of wires.
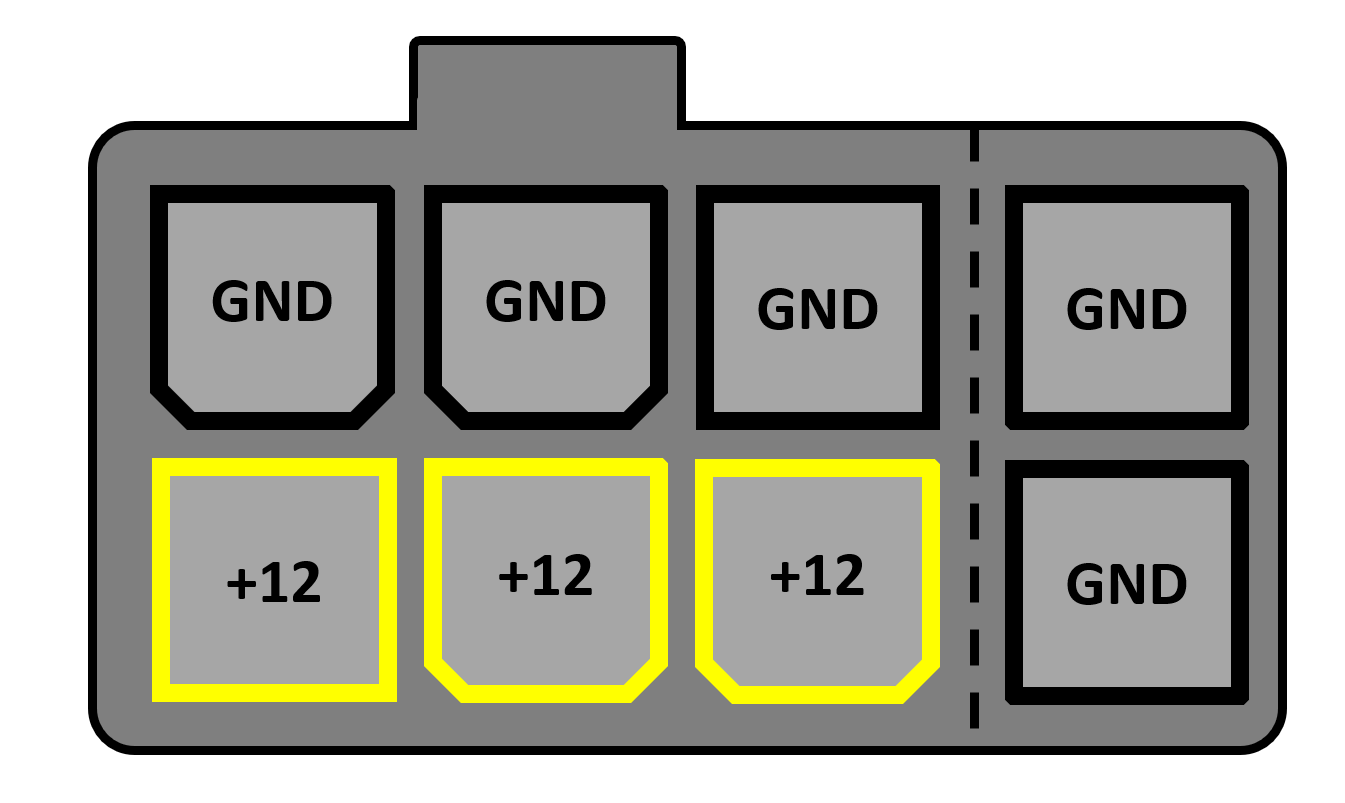
The difference between the half dozen and eight-pin PCI Express connector, is an extra two ground wires. This allows a higher level of current to flow down the +12V wires, helping to feed hungrier GPUs.
Over the past few years, nosotros've seen an increase number of ability supply units proudly article of clothing a tag of 'modular' in their description. All this means is that some of the power connectors are wired to another connector, that slots direct into the PSU. Then instead of having a mass of cables and connectors clogging up the within of the computer example, you lot tin remove what don't need to save some infinite.

This Libation Master model, like many others, uses a fairly basic connectedness system for the modular cables.

Each connector provides one each of +12V, +5V, and +3.3V wires, along with two footing wires, and depending on what device the cable is going to be fastened to, the connector at the other stop of the cablevision will either use the same wiring configuration, or something simpler.
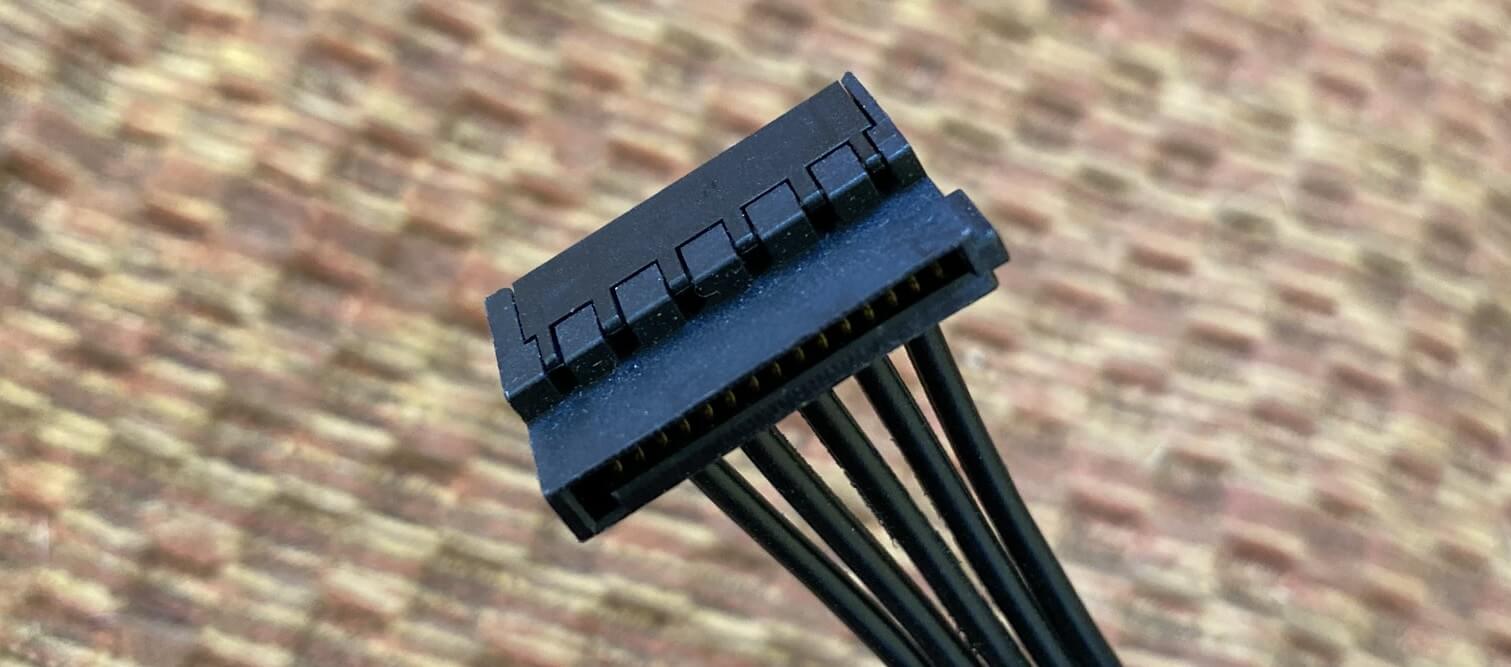
The Series ATA (SATA) connector in a higher place is used to provide power for hard drives, solid state drives, and peripherals such as DVD burners.
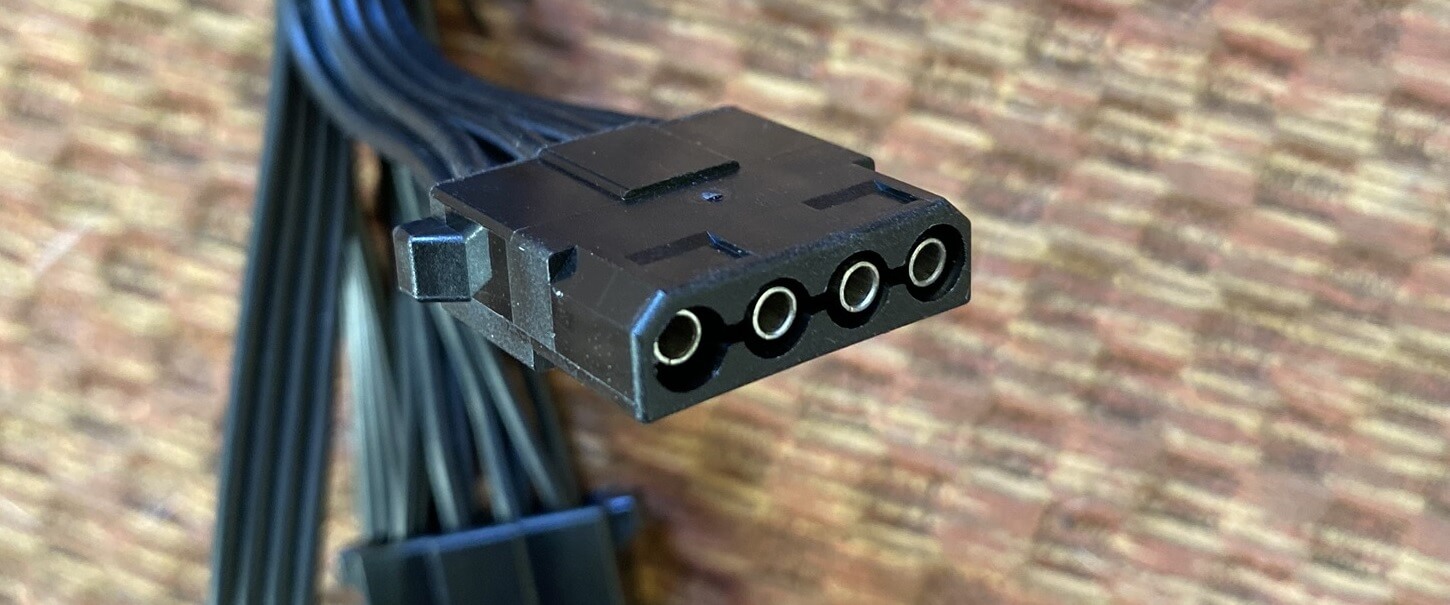

This familiar shape goes by the snappy name of an AMP MATE-N-LOK 1-480424-0 power connector. Well, nigh people telephone call it a Molex connector, but that's actually the name of the visitor that adult it. It provides one +12V, one +5V, and two ground wires.
The output supply cabling of a PSU is another area where costs can be saved or given a higher budget, either to ameliorate looks or flexibility of the wires. The thickness (or gauge) of the metal wire used in the cables plays a function, likewise, as thicker wires take less electrical resistance than thinner ones, which results in less heat existence generated as current flows through them.
(Something inside) Then stiff
At the beginning of this article, we said that most power supply units are named after the maximum amount of power they can offer. At the simplest level, electrical power is only voltage multiplied by current (e.g. 12 volts x 20 amps = 240 watts) and while such a argument will have many engineers chomping at the bit to correct this remark, it works well enough for our purposes.
Similar most branded or generic models, our PSU comes with a label providing diverse snippets of information most how much power each voltage line can provide.

Here nosotros can see that the total power bachelor from all the +12V lines added together peaks at 624 W; add together in all the others stated on the characterization and nosotros get a total of 760 W, and so what gives? Well, it'south downwards to the fact that the normal +5V and +3.3V lines are created using VRMs off the +12V output of the PSU.
And, of class, all of the output voltages come from a unmarried source: the mains outlet. So the rating of 650 W is the maximum the PSU can provide equally a total beyond all lines. So if you were using 600 W on the +12V output, you'll only have 50 Due west left for everything else. Fortunately, the majority of hardware inside a modern PC takes the bulk of its power off the 12V lines anyway, and so it's rarely a problem bold yous've picked the right PSU model for your needs.
Next to the power specifications, there's a characterization saying "80 Plus Bronze." This is an efficiency rating used in the manufacture in an entirely voluntary way (i.e. at that place are legal requirements for PSU manufacturers to comply with the rating organisation). The efficiency also depends on what size of load the PSU is attempting to serve (i.east. how much current is being drawn downwardly the various lines) .
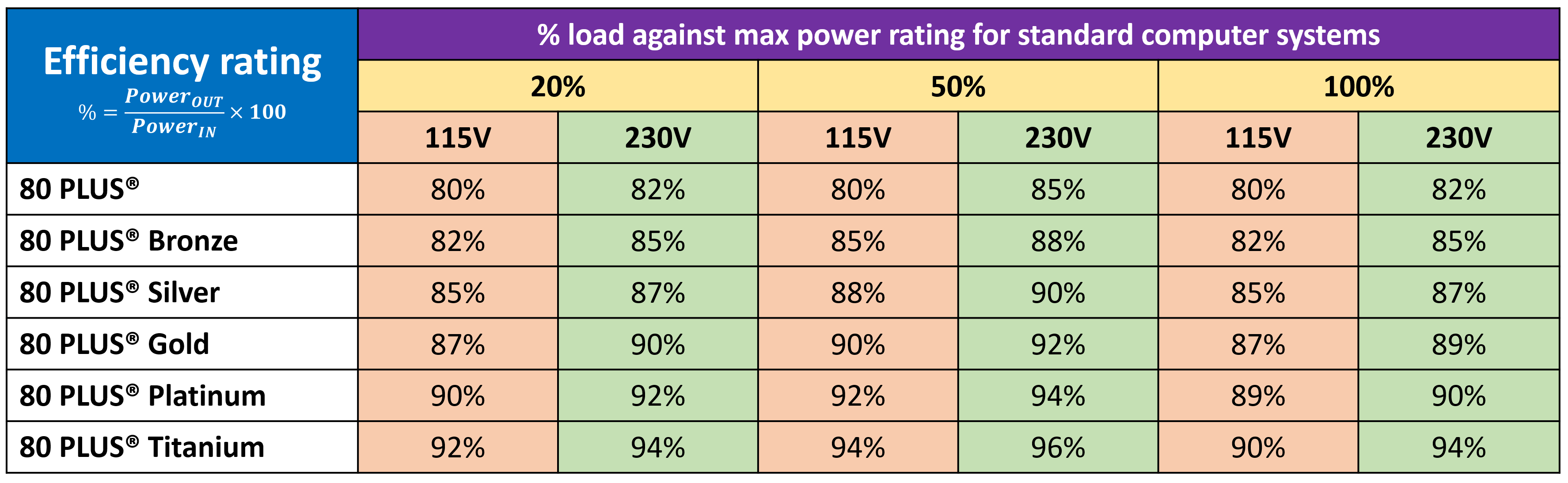
If we take our Cooler Main unit, running so that it'due south providing 325 Westward of ability (50% of its max rating), then we can expect it to accept an efficiency of 80 to 85%, depending on the mains supply voltage.
This would event in the unit drawing 382 to 406 Westward from the wall outlet. A higher lxxx PLUS rating doesn't hateful the PSU gives you more power, information technology just wastes less during all the filtering, rectifying, switching, and transforming stages.
As well note that the peak efficiency is somewhere between 50 and 100% loading; some manufacturers provide charts showing how you lot can expect the unit of measurement to perform nether different loads and supply voltages.
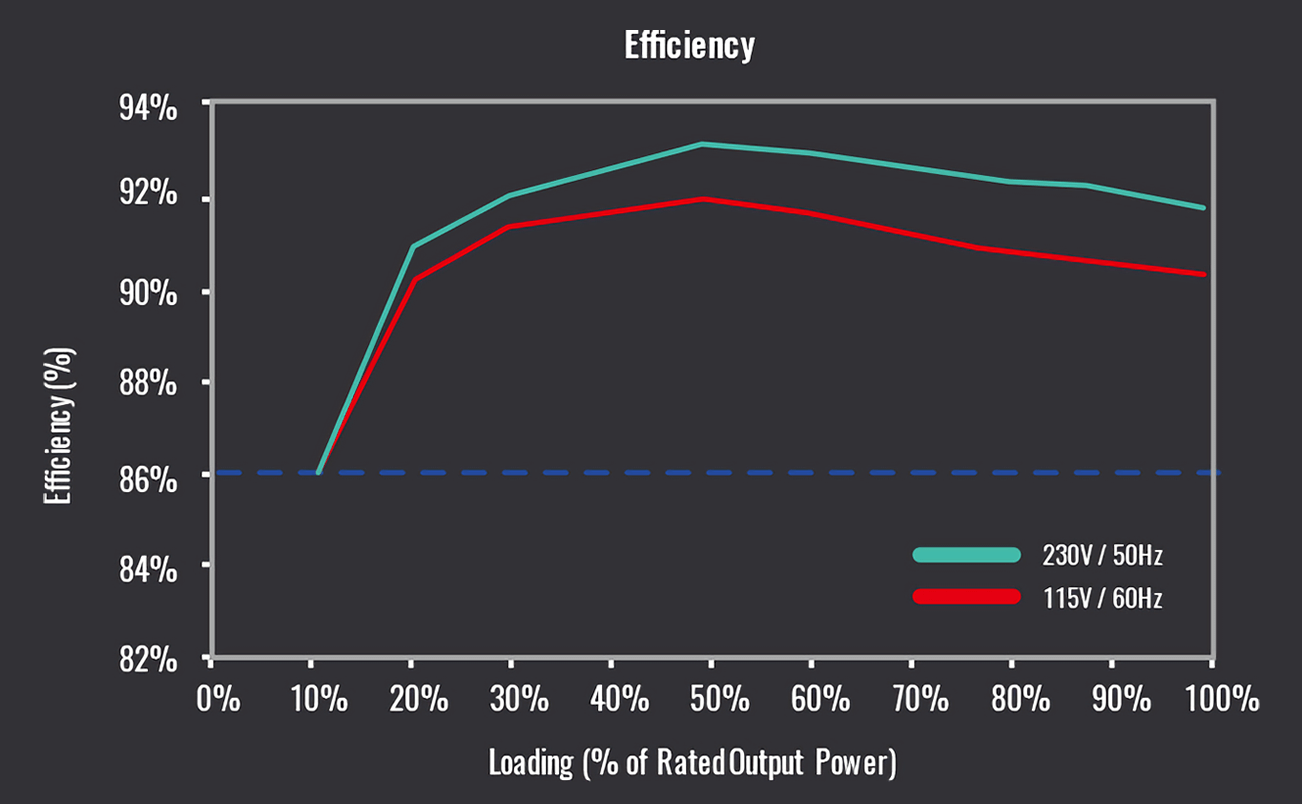
It's worth paying attention to this data sometimes, especially if you lot've tempted to lay downwardly a stack of bucks on a 1000 W PSU. If your computer is going to use anywhere near that power level, so its efficiency is going to accept a scrap of a sting.
Y'all might see some PSUs claiming to be single track or multi-rail (or offer a switch to flip between the ii). The term rail is only another word for the specific voltage that the power unit of measurement generates. Our Cooler Master case has a single 12 volt rail and all the diverse power connectors that provide +12V draw current off that rail, if used. A multi-rails PSU will have two or more systems providing the 12 volts - however, there's a big difference in how this is implemented.
PSUs for data center applications or compute servers volition take multiple rails for fault tolerance, and then if ane fails, it won't affect the others. A desktop computer with a multi-rail PSU might have such a setup, but they're more likely to be just taking the master 12V output and splitting it in ii or 3. For example, our example provides up to 52 amps of current off the +12V line, equating to 624 watts of electric power. A cheap multi-track version of the same unit might have 2 +12V lines shown in the specification, but each volition merely provide 26 amps of electric current (or 312 Due west).
A well designed desktop calculator PSU, using quality components, doesn't require a multi-rail +12V system, so don't worry about it!
Coin for nix?
Power supply units come in all kinds of toll tags. A quick run through the listings on Amazon, for the aforementioned size format, has them as low as $15 for a generic 400 W unit, and all the way upwards to $180-240 for a fully modular chiliad West nuclear power station from EVGA or Seasonic. What are you getting for your money? What sort of things toll over $200?
The ability to deliver more power is the obvious one, but it'south how that ability gets delivered. The ultra cheap model permits up to 25A of current on the +12V lines, whereas the wallet buster provides over 3 times more, at 83A. Today'due south CPUs and graphics cards use the +12V lines for about all of their power requirements, but surely 25A is enough?

Given that y'all tin now buy a 'desktop' CPU with 32 cores and pair information technology with an equally titanic graphics card, both with an appetite for 300W at total load, the inexpensive PSU admittedly would not be up to the demand; on the other hand, though, the near expensive 1 would have plenty of headroom to cope. And since the combined toll of such a CPU and GPU could hands peak $3,500 or more, shelling out a few extra hundred possibly isn't going to exist much of a shock for some customers.
But what you're really paying for is the quality of the components used inside the PSU. Go back to the kickoff of this commodity and expect at the guts of the Cooler Primary unit we've been taking apart. At that place's not a massive corporeality of parts in that location, and since nigh every bit is critical to the operation of the device, it'south non hard to see why spending more than is not always money for zippo.
And with that, we bring our dissection of the PSU to a close (and exit a trail of bits all over the flooring). It's a fascinating piece of a kit and the level of engineering involved in designing and manufacturing a skilful one is surprisingly complex. If yous've got whatsoever questions about ability supply units or the i currently sitting in your computer, quietly doing its task, fire them our way in the comments section below equally usual. Stay tuned for more anatomy series features.
Shopping Shortcuts
(Picks from TechSpot staff, from to the lowest degree to more expensive):
- Thermaltake Smart 600W on Amazon
- EVGA 600 BR on Amazon
- Cooler Chief MasterWatt 750 W on Amazon
- Corsair RM750 750 W on Amazon
- SilverStone Strider ST80F 800 W on Amazon
- Seasonic Prime PX-1000 W on Amazon
Source: https://www.techspot.com/article/1967-anatomy-psu/
Posted by: adkinscomay1980.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Is 414w Draw To Close To A 500w Power Supply?"
Post a Comment